Atlantic Salmon
Atlantic Salmon Hatching Process
Explore UK Fish Production Insights
Learn How to Optimise Hatchery Losses
Access Expert Strategies for Successful Aquaculture
Production Overview
Atlantic salmon is one of the most significant fish species in aquaculture, particularly in the UK. In 2020, global production of Atlantic salmon reached 2.7 million tonnes, with the UK contributing 192,000 tonnes to this total.

Survival Rates and Losses
Survival Rates:
Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) egg survival rates typically range from 60% to 90% under optimal water quality, broodstock health, and controlled environmental conditions. Proper management of temperature and oxygen levels is crucial for maximizing survival.
Losses:
Egg losses, which can reach up to 30%, are primarily caused by fungal infections, poor water quality, and handling stress. Factors like overcrowding and mechanical damage during transportation further contribute to mortality.
Economic Impact:
High egg mortality leads to reduced fry production, increased operational expenses, and financial losses for aquaculture farms. Implementing advanced monitoring technologies helps mitigate risks and enhance profitability.
Overall Challenges
Several factors contribute to losses in salmon production:
- Disease Outbreaks: Bacterial and viral infections are significant threats that can rapidly decimate stocks.
- Poor Water Quality: Issues with oxygen levels and temperature fluctuations increase stress and susceptibility to disease.
- Predation: Hatchery life stages are particularly vulnerable to predators.
- Genetic Factors: Certain genetic predispositions can impact survival rates and growth.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Poor nutrition can lead to developmental issues and weakened immune systems.
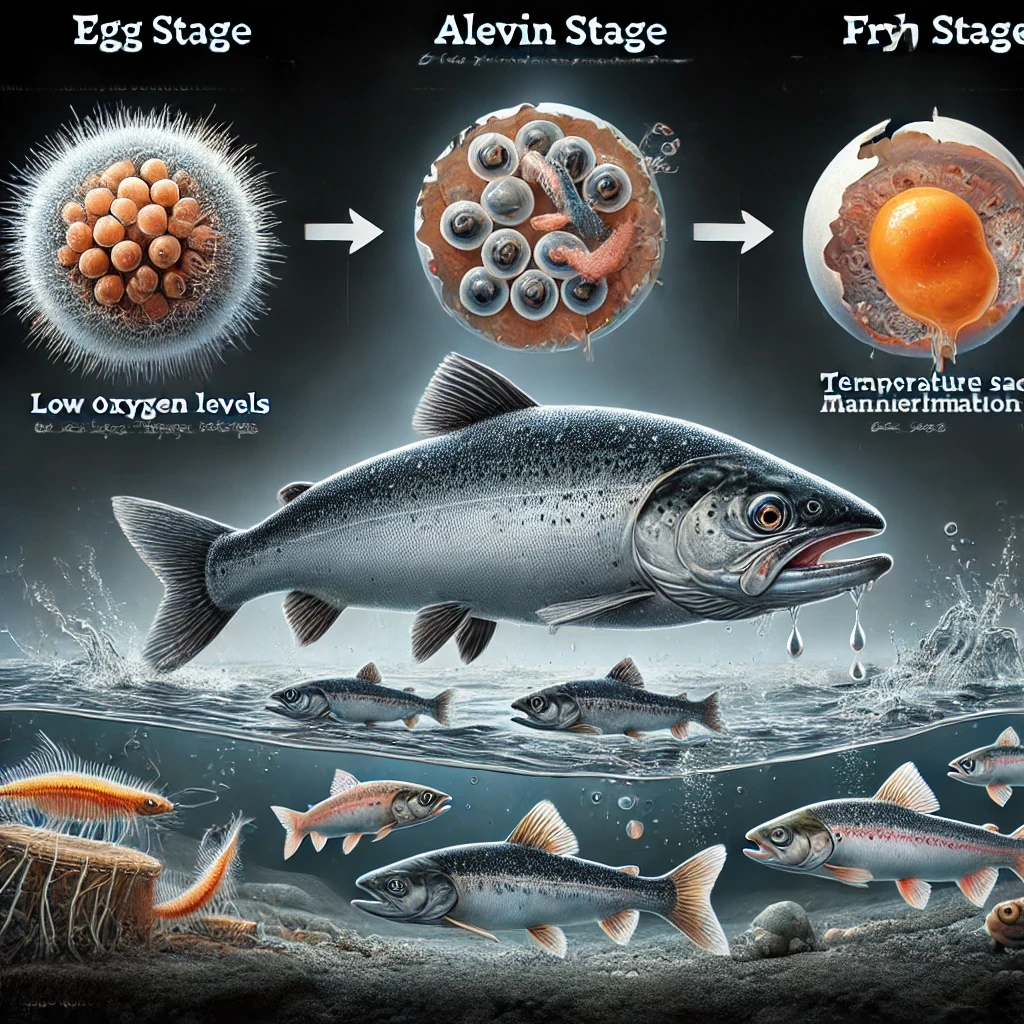
Challenges in Hatchery Life Stages
- Fungal Infections: These are common and often exacerbated by poor water quality.
- Oxygen Deprivation: Low oxygen levels can significantly impact egg viability.
- Temperature Fluctuations: Unstable temperatures can lead to high egg mortality.
- Yolk Sac Malformation: This issue can hinder proper feeding and growth.
- Disease Susceptibility: Fry is highly vulnerable to infections.
- Cannibalism: Cannibalism among fry can lead to further losses.
- Nutritional Management: Precise nutrition is critical to ensure healthy development.
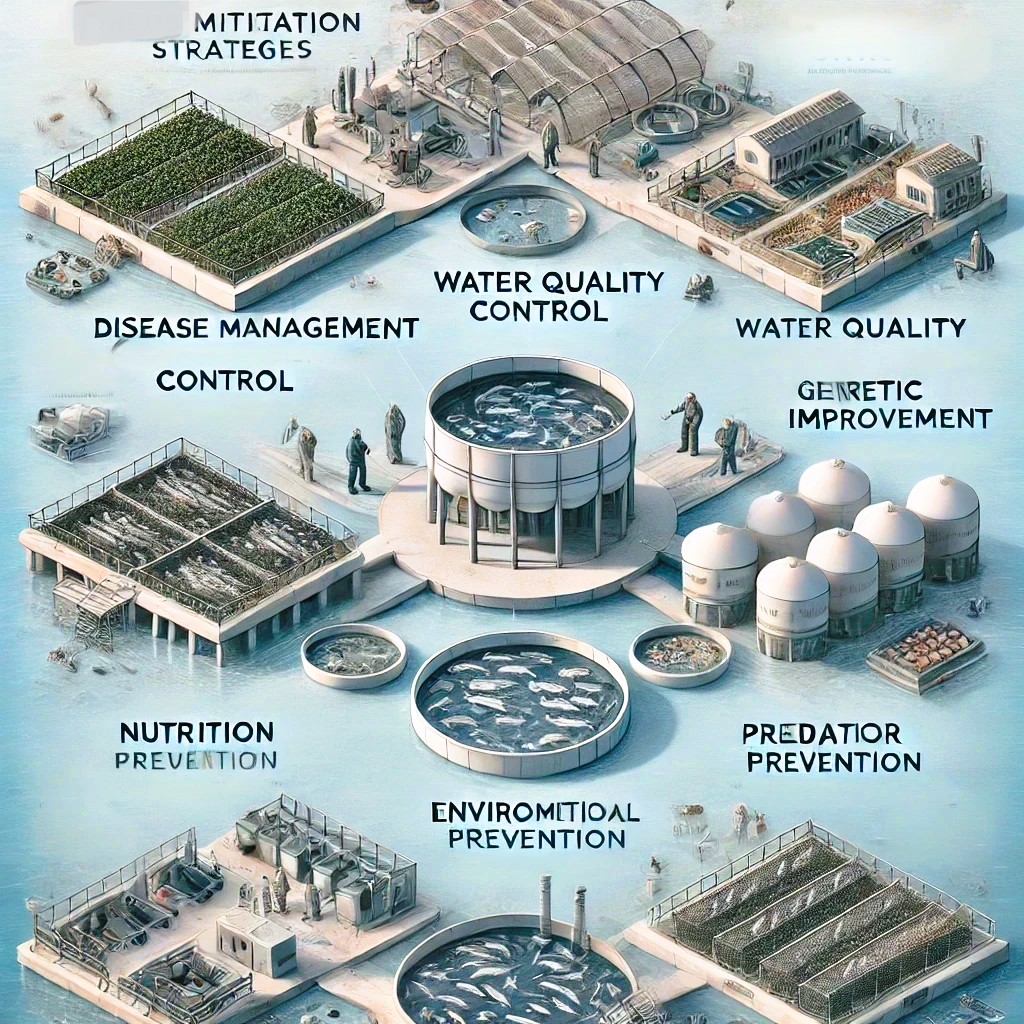
Mitigation Strategies
To mitigate these challenges, salmon farmers and hatcheries employ various strategies:
- Disease Management: Biosecurity measures, vaccination programs, and regular health monitoring are essential.
- Water Quality Control: Advanced filtration systems and recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS) help maintain optimal water conditions.
- Nutrition: Stage-specific feed formulations and precise feeding schedules are implemented to support growth and health.
- Genetic Improvement: Selective breeding and genomic selection enhance disease resistance and growth rates.
- Environmental Control: Maintaining proper temperature, oxygen levels, and stocking densities is crucial.
- Predator Prevention: Physical barriers and deterrent systems protect salmon stocks.
How AIquaboost Can Help
By integrating AIquaboost into your hatchery operations, you gain access to:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Continuous tracking of key water parameters.
- Predictive Analytics: Early warnings for potential issues like temperature spikes or pathogen outbreaks.
- Resource Optimization: Smart management of aeration, water flow, and heating systems to lower costs.
- Actionable Insights: Data-driven recommendations to improve egg survival rates and overall hatchery performance.
Enhance Atlantic Salmon Survival with AIquaboost
AIquaboost provides advanced, data-driven solutions to help salmon farms optimize survival rates and overall production efficiency. Our intelligent aquaculture management system focuses on improving water quality, disease prevention, and operational precision to ensure healthier fish and higher yields.
Get in touch with us today to see how AIquaboost can revolutionize your Atlantic salmon farming operations and drive sustainable growth.